
 This
is a very old independent suspension, used by some sports cars since
the
50s, such as VW Beetle, Porsche 356 (which was based on Beetle) and
Mercedes'
famous 300SL Gullwing (1954). However, it disappeared for at least 2
decades
because it has so much weakness. The only advantage is - it provides
independent
shock absorption.
This
is a very old independent suspension, used by some sports cars since
the
50s, such as VW Beetle, Porsche 356 (which was based on Beetle) and
Mercedes'
famous 300SL Gullwing (1954). However, it disappeared for at least 2
decades
because it has so much weakness. The only advantage is - it provides
independent
shock absorption.
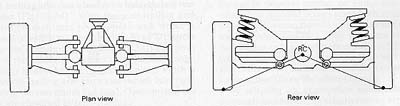
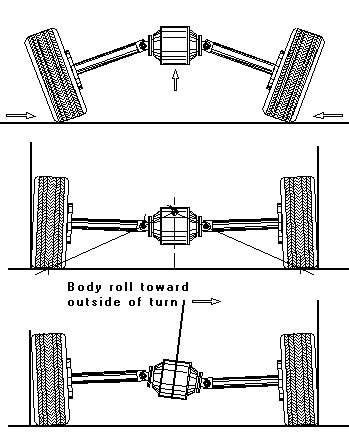
Handling is really awful, as camber angle can be noticeably changed by bouncing motion (as shown in the first picture), change of static weight of the car (second picture) and body roll (third picture). Especially is the body roll, which makes both wheels lean towards the corner, thus result in severe oversteer. This explain why the Mercedes 300SL Gullwing was criticised as very unpredictable and difficult to handle.
Camber variation can be reduced via using longer swing arms, but this could create problems in packaging. It engages the space for rear seats and even the boot.
Another solution is
to introduce
inherent understeer by setting the wheels negative cambered. This could
compensate the oversteer during cornering but the drawback is the
instability
in straight line. To cars as slow as VW Beetle, swing axle shows its
advantage
in ride comfort over contemporary non-independent suspensions while the
weakness in handling is not easily seen. For Porsche 356, at least in
the
less-powerful early versions, the problem is not severe, too. In later
years, when the car got bigger and bigger engine, Porsche realised that
the days for swing axle had nearly finished. That came true when the
911
launched in 1963, used trailing arm at the rear instead of swing axle.
| Advantage: | Independent ride. |
| Disadvantage: | Very bad handling. |
| Who use it ? | Mercedes 300SL (1954), VW Beetle, Porsche 356 etc. |
 To
many suspension designers, double wishbones (or "A-arms") is the most
ideal
suspension. It can be used in front and rear wheels, it is independent
and most important, it has near perfect camber control. For 40 years
and
even today, this is the first choice for racing cars, sports cars and
demanding
sedans.
To
many suspension designers, double wishbones (or "A-arms") is the most
ideal
suspension. It can be used in front and rear wheels, it is independent
and most important, it has near perfect camber control. For 40 years
and
even today, this is the first choice for racing cars, sports cars and
demanding
sedans.
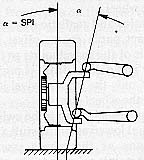
Basically, double wishbones suspension always maintains the wheel perpendicular to the road surface, irrespective of the wheel's movement. This ensure good handling.
Traditional double
wishbones
consists of 2 parellel wishbone arms of equal length, which has the
drawback
of excessive tire scrubbing because of the large variation in track
width
as the wheel moved off the neutral position. Therefore engineers
developed
unequal-length non-parellel
A-arms
to solve this. By tilting the upper A-arm, anti-dive function is also
achieved.
 |
<<
Porsche 993's
rear suspension
Double wishbones suspension has been very popular in American cars. Not so in Europe because cars in there are smaller thus cannot accommodate this relatively space-engaging suspension. Besides, it is more costly than MacPherson strut and torsion beam because it involves more components and more suspension pick up points in the car body. Owing to these reasons, very few small cars adopt it. One of the few examples is Honda Civic. This does not mean American cars have better handling. No, due to their larger size and weight and the less effort spent in suspension tuning, the majority of double wishbones-equipped American cars actually handles worse. |
| Advantage: | Ideal camber control leads to good handling. |
| Disadvantage: | Space engaging and costly. |
| Who use it ? | American sports cars and some sedans, most European pure sports cars like Ferrari, TVR, Lotus .... some Euopean sedans, most Honda .... many many many. |
 The MacPherson strut suspension was invented in the 1940s by Earl S.
MacPherson
of Ford. It was introduced on the 1950 English Ford and has since
become
one of the dominating suspensions systems of the world because of its
compactness
and low cost.
The MacPherson strut suspension was invented in the 1940s by Earl S.
MacPherson
of Ford. It was introduced on the 1950 English Ford and has since
become
one of the dominating suspensions systems of the world because of its
compactness
and low cost.
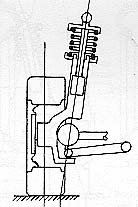
Unlike other suspension designs, in MacPherson strut suspension, the telescopic shock absorber also serves as a link to control the position of the wheel. Therefore it saves the upper control arm. Besides, since the strut is vertically positioned, the whole suspension is very compact. To front-wheel drive cars, whose engine and transmission are all located inside the front compartment, they need front suspensions which engage very little width of the car. Undoubtedly, MacPhersion strut suspension is the most suitable one.
Nevertheless, this
simple
design does not offer very good handling. Body roll and wheel's
movement
lead to variation in camber, although not as severe as swing axle
suspension.
From a designer's viewpoint, its relatively high overall height
requires
a higher hood and fender line, which is not very desirable to sports
cars'
styling.
 |
<<
Hyundai Atoz's
MacPherson strut
Like double wishbones suspension, MacPherson strut can be adopted in both front and rear wheels. In the 80s, there are many budget sedans employed Mac strut in all corners, the most famous is Fiat's Type 4 and Tipo platforms, on which Fiat Croma, Lancia Thema, Saab 9000, Fiat Tipo, Tempra, Lancia Delta, Dedra etc. were based. None of them was famous of handling. Basically, Alfa Romeo's GTV / Spider is also based on the Tipo platform, however, after experienced unsatisfatory handling during testing, the rear MacPherson struts were replaced by the pricier multi-link suspensions. |
| Advantage: | Compact and cheap. |
| Disadvantage: | Average handling. |
| Who use it ? | Most front-wheel drive compact cars. |